If You Have Questions Please, Contact Us

Are you struggling to manage your restaurant? Are you tired of keeping track of orders, inventory, and employees manually? Then it’s time to upgrade to a Point of Sale (POS) system. A POS system can help you streamline your restaurant operations, reduce errors, and increase profitability. In this article, we’ll discuss how you can manage your restaurant with the best POS system for restaurant.
Restaurant POS software is designed to automate and streamline restaurant operations by managing sales transactions, inventory, and other key aspects of the business. It allows servers to take orders quickly and accurately, process payments securely, and manage inventory levels in real time. Additionally, POS software can help with menu management, allowing restaurants to easily update and modify their menu items, prices, and descriptions. With powerful reporting and analytics capabilities, POS software can also provide valuable insights into key metrics such as sales, inventory, and labor costs. Overall, best restaurant management software can be a valuable asset for any restaurant owner looking to improve their operations and increase profitability.
There are many Restaurant pos system features, such as:
A POS system can help you streamline your restaurant operations by automating processes such as order taking, payment processing, and inventory management. This can help reduce errors, improve efficiency, and increase productivity.
Customer service is one of the restaurant pos system features that can help you improve customer service by enabling you to take orders quickly and accurately. It can also provide you with insights into customer preferences and behaviors, allowing you to tailor your offerings to their needs.
A POS system can help you increase profitability by reducing waste and theft. It can also provide you with insights into your business performance, allowing you to identify areas where you can cut costs or increase revenue.
Another of the restaurant pos system features is simplifying accounting taxes, and inventory. This can help reduce the risk of errors and save you time and money.
Choosing the best POS system for restaurant can be a daunting task, as there are many options available on the market. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a POS system:
Make sure the POS system you choose has all the features you need to manage your restaurant. These may include order taking, payment processing, inventory management, customer management, and reporting.
Compatibility is another important factor to consider when choosing the best POS system for restaurants. It’s important to select a system that is compatible with your existing hardware and software, such as your point-of-sale terminals, payment processing systems, and inventory management tools. This can help to ensure a smooth implementation process and minimize disruptions to your business operations.
Ease of use is a critical factor when choosing the best POS system for restaurants. A system that is intuitive and easy to navigate can help to reduce training time, minimize errors, and improve overall efficiency. When evaluating different POS systems, it’s important to consider factors such as the user interface, available training and support resources, and the system’s overall ease of use.
Consider the cost of the POS system, including hardware, software, and ongoing support and maintenance. Make sure that the system provides good value for money and fits within your budget.
Customer support is crucial when selecting the best POS system for restaurants. Look for a provider with a strong track record of customer service and support, with easily accessible resources to help you troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
MatixPOS Restaurant Management a Complete POS with Recipe Management & Food Costing. Having your eyes on business performance anytime and at any POS locations. Manage big or small restaurants or franchises involves operations like billing, inventory, costing, accounting and many more.
In conclusion, managing a restaurant can be a challenging task, but a restaurant pos system features can help you streamline operations, improve customer service, increase profitability, and simplify accounting. These are some of the most important restaurant pos system features, When choosing a POS system, it’s important to consider factors such as features, compatibility, ease of use, cost, and customer support. By selecting the best POS system for restaurant, you can take your business to the next level and achieve greater success.
In the world of business, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software has become an essential tool to manage different business functions. Odoo ERP is one such software that has gained immense popularity in recent years. In this article, we will discuss what Odoo ERP is, and we will explore benefits of Odoo ERP.
Odoo ERP Implementation is an open-source ERP software that enables businesses to manage their operations efficiently. It offers a range of business applications that are integrated, providing a comprehensive solution for all business needs. Odoo ERP was initially released in 2005 under the name TinyERP and was later renamed Odoo in 2010.
Odoo ERP features
Below we will mention to you some of the main benefits of Odoo ERP:
Odoo ERP provides customizable dashboards that allow users to view the data that is most important to them. Users can drag and drop different elements to create their personalized dashboard, which can display charts, graphs, or tables.
One of benefits of Odoo ERP is sales management has a sales management module that enables businesses to manage their sales processes efficiently. The module allows businesses to track leads, manage quotations, and process orders. Users can also create reports to analyze sales data.
Odoo ERP provides a comprehensive inventory management module that allows businesses to manage their inventory efficiently. The module enables businesses to track inventory levels, create purchase orders, and manage stock movements.
Odoo ERP has a robust accounting and finance module that provides a range of features, including invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. The module also supports multiple currencies and languages.
Odoo ERP provides a human resources management module that enables businesses to manage their HR processes efficiently. The module allows businesses to manage employee data, track attendance, and process payroll.
benefits of Odoo ERP has a project management module that allows businesses to manage their projects efficiently. The module provides features such as task management, project planning, and time tracking.
One of Odoo ERP features is e-commerce and the Odoo system has an e-commerce module that enables companies to create and manage their online stores. The module provides features such as product catalog management, payment processing, and order management.
Odoo ERP provides a marketing automation module that allows businesses to automate their marketing processes. The module enables businesses to create targeted campaigns, track campaign performance, and analyze marketing data.
Odoo ERP has a comprehensive CRM module that enables businesses to manage their customer relationships effectively. The module provides features such as lead tracking, customer data management, and sales forecasting.
Odoo ERP provides a range of reporting and analytics tools that enable businesses to gain insights into their operations. The software allows users to create customized reports and dashboards that provide real-time data.
Odoo ERP is a comprehensive business management software that integrates all aspects of a company’s operations, including sales, inventory, accounting, and manufacturing. Its relevance in business lies in its ability to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and provide real-time visibility into key business metrics. With Odoo ERP, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and make better-informed decisions. Additionally, its modular design allows for customization to fit the unique needs of each business. Overall, Odoo ERP is a powerful tool that can help businesses of all sizes succeed in today’s competitive marketplace.
Read More: What is ERP?
Before starting to use Odoo ERP, businesses should consider a few important steps. First, they should define their business processes and identify the areas where benefits of Odoo ERP can help improve efficiency. Next, they should evaluate the modules available in Odoo ERP and select the ones that are relevant to their business needs. Then, they should ensure that they have the necessary hardware and software infrastructure in place to support the implementation of Odoo ERP. Finally, they should train their employees on how to use the software and how it can benefit their day-to-day work. By taking these steps, businesses can maximize the benefits of using Odoo ERP and ensure a successful implementation.
One of benefits of Odoo ERP that can help companies maximize ROI by streamlining their operations and providing real-time visibility into key business metrics. With Odoo ERP, businesses can automate workflows, reduce manual data entry, and eliminate redundant tasks, which can increase productivity and efficiency. Additionally, Odoo ERP provides detailed reporting and analytics, allowing companies to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions. By optimizing their operations and making informed decisions, companies can reduce costs, increase revenue, and ultimately maximize their ROI. Odoo ERP’s modular design also allows for customization to fit the unique needs of each business, further enhancing its ability to help companies achieve their financial goals.
In conclusion, Odoo ERP is a comprehensive business management software that integrates various modules to help businesses streamline their operations and achieve their goals. Benefits of Odoo ERP include increased productivity, efficiency, real-time visibility, automation, customization, and data-driven decision-making. Odoo ERP’s modular design allows for customization to fit the unique needs of each business. With Odoo ERP, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, increase revenue, and ultimately succeed in today’s competitive marketplace.
The three financial statements – the balance sheet, the income statement, and the cash flow statement – all serve different purposes. One might be more suited to determine the company’s profitability, and another might be better for showing the company’s assets. They should all be studied together because they are connected, and by analyzing these relationships, investors are able to uncover the economics of particular businesses and decide if purchasing or selling them are prudent choices.
ʻʻThe income statement measures the results of operations during the periodʼʼ
The income statement is an important financial report that shows an enterprise’s success in terms of profitability. Unlike the balance sheet the income statement is prepared for a given period such as a quarter or a year, versus a snapshot on a particular day
The preparation of this financial report is based on the following formula:
Revenues – expenses = profit or loss
If the business brings in more revenues than it pays out in expenses, it reports a profit. Otherwise, it reports a loss. The following is a sample income statement.
Revenues: Revenues article Revenue – Cash inflows of assets of an entity during a period from rendering services, producing or delivering goods, or other activities that constitute the entity’s ongoing main operations.
It is often given as sales discounts sales minus, allowances and returns. Each time a company performs a service or sells a product, it obtains revenue. This usually is mentioned as sales revenue or gross sales.
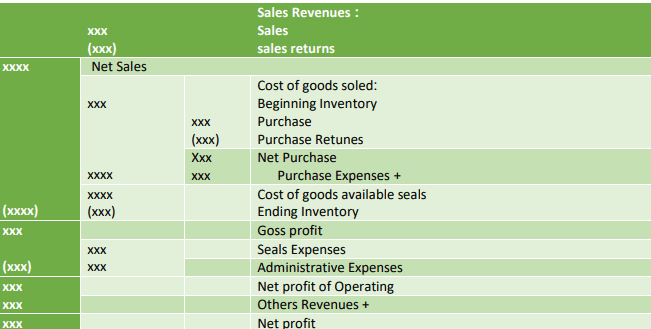
Expenses: Cash outflows or other using up of incurrence or assets of liabilities during a period from rendering services, producing or delivering goods, or carrying out other activities that constitute the entity’s ongoing major of the company.
The Profit and Loss account summaries a firm’s trading results over a period and shows how the resulting profits were used, or how the losses were financed. The profit and loss account tends to have more value to the managers of the firm than the balance sheet that is directed more at those outside reviewing the firm. It covers the profits and losses usually over a period of a year, larger businesses often produce them half-yearly or quarterly. The most features of a profit and loss account are
1. Sales revenue fewer costs = profit this is the basic equation that underpins the profit and loss account. Revenue can cover a wide range of activities, investments, sales receipts, cash transactions, etc. Sales revenue excludes any benefit tax.
2. The cost of goods sold is the first group of subtractions, which is about how much it cost you to produce the goods and services that generated the revenue. It includes all costs related to the product (often called production costs). So direct materials, direct labor, plus all overhead costs that can be allocated to the production process.
.3 Gross profit is the sum remaining when you have deducted the cost of goods sold from sales revenue
Income statements help investors and Creditors to determine the past financial performance of the enterprises, assess the capability of generating future cash flows through reports of the expenses and income, and predict future performance.
Information on an income statement contains several limitations: Items that might be relevant but cannot be reliably measured (e.g. brand recognition and loyalty) are not reported.
Some numbers depend on accounting methods used (e.g.to measure inventory level using FIFO or LIFO accounting).
Some numbers in income statements rely on estimates and judgments (e.g. depreciation expense depends on salvage value and estimated useful life).
Guidelines for statements of comprehensive income and income statements of business entities are formulated by the IFRS IFRS article International Accounting Standards Board and numerous country-specific organizations, as an example: in some companies, Names and usage of various accounts within the income statement depend on the kind of organization, industry practices and therefore the requirements of various jurisdictions. If applicable to the business, summary values for the following items should be included within the income statement.
Operating section: Revenue – Expenses – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Cost of Sales
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Cost of Sales: represents the direct costs attributable to goods produced and sold by a business (merchandizing or manufacturing). It includes direct labor, material costs, and overhead.
See: Real Difference between Expenses and Cost of Goods Sold Operating expenses article
IFRS is an international accounting framework, a set of accounting standards developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). Correctly organize and report financial information. It is derived from the statement of the London International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
Currently, this is the accounting framework required by most countries around the world. IFRS requires companies to report their financial performance and financial status using the same rules; this means that unless any fraudulent operations are performed, the financial reports of all companies that use IFRS are quite uniform, which makes comparison and comparison of their financial The result becomes easier.
IFRS 9 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018 with early application permitted.
IFRS 9 specifies how an entity should classify and measure financial assets, financial liabilities, and some contracts to buy or sell non-financial items.
IFRS 9 requires an entity to recognize financial assets or financial liabilities in its statement of financial position when it becomes a party to the terms of a financial instrument contract. At initial recognition, the entity measures the financial assets or financial liabilities at their fair value plus or minus; for financial assets or financial liabilities that are not measured at fair value and whose changes are included in the current profit or loss, they are directly attributed to the financial asset or financial liability Transaction costs. Purchase or issue financial assets or financial liabilities.
Financial assets When an entity first identifies a financial asset, it classifies it based on its business model for managing assets and the contractual cash flow characteristics of the asset, as follows:
Amortized costs of financial assets that meet the following two conditions are measured at amortized cost: Assets are held in a business model whose purpose is to hold assets to collect contractual cash flows; and
The contractual terms of financial assets generate cash flow on a specified date, which is only the payment of principal and outstanding principal interest.
– The fair value measured through other comprehensive income-If a financial asset is held in a business model that achieves its goal by collecting contractual cash flows and selling financial assets, it is classified and measured at fair value through other comprehensive income.
– Measured at fair value and its changes are included in the current profit and loss-Any financial assets that are not held in one of the above two business models are measured at fair value and their changes are included in the current profit and loss.
When and only if an entity changes its business model for managing financial assets, it must reclassify all affected financial assets.
IFRS 15 takes effect during the annual reporting period beginning on or after January 1, 2018, allowing early application.
IFRS 15 establishes the principles that entities apply when reporting information about the nature, amount, time, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows from contracts with customers. According to IFRS 15, an entity recognizes revenue in an amount that reflects the consideration that the entity expects to be entitled to in exchange for these goods or services, to express the transfer of promised goods or services to customers.
Read More: What is ERP System?
In order to recognize revenue based on IFRS 15, entities should use the following five steps:
-Determine the contract with the customer.
-Determine the performance obligations in the contract. Performance obligations are commitments to transfer significantly different goods or services to customers in the contract.
-Determine the transaction price. The transaction price is the amount of consideration that the enterprise expects to transfer the consideration goods or services to the customer in exchange. If the consideration promised in the contract includes a variable amount, the entity must estimate the consideration it is expected to be entitled to in exchange for transferring the promised goods or services to the customer.
IFRS 16 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2019, and allows early adoption (as long as IFRS 15 is also adopted).
The purpose of IFRS 16 is to report the following information: (a) faithfully represent the lease transaction, and (b) provide a basis for financial statement users to evaluate the amount, timing and uncertainty of the cash flow generated by the lease. To achieve this goal, the lessee should recognize the assets and liabilities arising from the lease.
IFRS 16 introduces a single lessee accounting model and requires the lessee to confirm all leased assets and liabilities for leases longer than 12 months unless the value of the underlying asset is low. The lessee must recognize the right-of-use asset on its behalf to use the underlying lease asset and the lease liability on its behalf to pay the lease payment obligation.
IFRS 17 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2021, and allows the simultaneous adoption of IFRS 9 and IFRS 15.
Insurance contracts have the functions of financial instruments and service contracts. In addition, the cash flows generated by many insurance contracts over a long period are highly variable.
After explaining all the IFRS standards our mission is to develop and provide an ERP software to manage IFRS that brings transparency, accountability, and efficiency to financial statements to raise understand the relationships between different accounts in your business.
Most business owners are often looking for a powerful system that can manage their enterprise, deal with their administrative workloads and provide them with accurate financial reports. If you seek to gather your company departments under one umbrella to ensure successful management and high levels of control, you are at the right place.
sismatix provides you with a bundle of modern solutions that will help you manage your project and give you precedence and excellence through providing an ERP system to manage the IFRS.
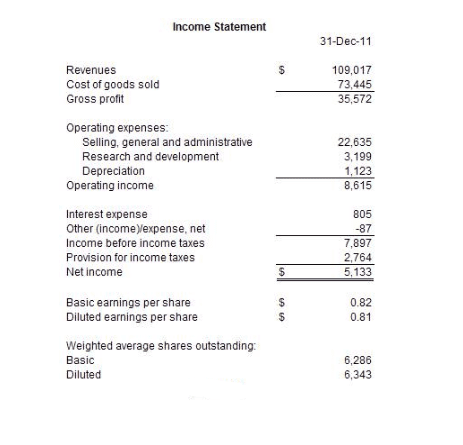
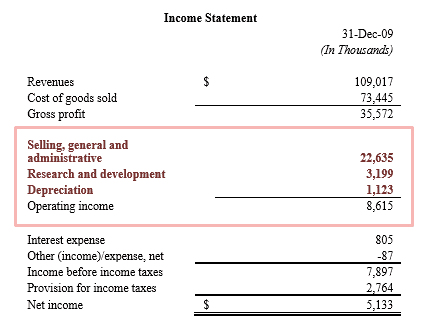
Operating expenses or OPEX refer to the expenditures associated with operating or running a business. They are necessary in order for the company to produce revenues. They are the muscle that makes things happen. Operating expenses consist of selling, general and administrative expenses (SG&A), research and development, and depreciation.
SG&A expenses are expenditures that are not directly tied to a service or product such as overhead costs.
Selling, general and administrative expenses (SG&A) include expenditures such as sales commissions, management salaries, office supplies, advertising, and accounting and legal fees. The amount of SG&A expenses does not mean much by itself but becomes more meaningful when compared either to total revenues or gross profits.
Generally, the best businesses spend fewer revenue dollars on these activities than their competitors do.
Some companies sell such a valuable product or service that they do not have to advertise much because customers do the selling through word of mouth. This is the best kind of advertising because it is free. If, on the other hand, a business is selling a product or service that is just average and people do not really need it, then a significant amount of resources needs to be spent convincing people to buy it.
The cost of goods sold represents the direct expenditures associated with manufacturing a product. These expenditures include the raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead. When reselling a product, the cost of goods sold represents the cost of purchasing it from the manufacturer. When the company provides a service instead of selling a product, the cost of goods sold is replaced with another term – the cost of revenue.
What is important to note is that the cost of goods sold only appears on the income statement when the company is actually “selling” or “reselling” its products or services. What if the company is not able to sell its products? The cost of goods sold does not appear on the income statement because the preparation of financial statements of publicly traded companies has to adhere to GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). Under GAAP, companies must follow accrual basis accounting, which means that expenses must be matched with corresponding revenues. If the company is not able to sell its products, it does not have any revenues for the corresponding costs to be matched to, and therefore, the production costs are not expensed through the cost of goods sold on the income statement. Investors can prevent unpleasant surprises by monitoring inventory levels on the balance sheet and comparing them to total assets and revenues. A significant accumulation of products in inventory without a similar increase in revenues may mean that the company is unable to sell it products, and as a result, may need to write down the inventory costs through the income statement as a loss without a corresponding increase in revenues.

Operating expenses and cost of goods sold measure various ways in which resources are spent in the process of running an operation.
When an income statement is generated, the COGS and operating expenses are shown as separate line items subtracted from total revenue or sales.
Read More: What is ERP System? What does it stand for and why should your business care about it?
MatixERP is a complete ERP software that is developed with great care to gather everything business managers need in one place.MatixERP helps you transform your business processes to meet today’s needs and tomorrow’s challenges.
By the end of this article, you will be know what is ERP and familiar with the definition of ERP system and how it’s going to affect the flow and management of different processes in any organization. In addition, you will know when to use an ERP system and how it’s going to be implemented and what are the industries that can implement an ERP solution.

ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. ERP system is a business process management software that allows an organization to use a system of integrated applications to manage the business and automate many back office functions related to technology, services and human resources.
Instead of relying on several software vendors with different standalone data vessels; ERP system relies on a centralized database to store and retrieve data in real time to manage day-to-day processes in different departments which keeps the integrity of data and eliminate data duplication.
History

what is ERP? In 1960s, the need to speed up the manufacturing processes and to balance the production with customer demands came up with creating a software known as MRP – Manufacturing Materials Planning. This type of computer software helped in manufacture planning, maintain stock levels and define purchase strategies.
Because of the improvements in hardware and mainframes developed by IBM in 1970s, MRP was implemented in several large manufacturing factories, and by the 1980s, especially after developing a financial management system for the first time, MRP got more capabilities and improvements, hence, it was named MRP II or Manufacturing Resource Planning.
By 1990s, the ERP term raised for the first time when these type of software systems were extended to not only manage inventory and production, but also to control and manage other functions such as Human Resources (HR) and Accounting to become that ERP we know this days.
Today’s ERP system is more advanced and complicated than ever for sure; it can be installed on premise with a centralized server in your company, or on the cloud. It can be a desktop application or web based application. Nowadays, some significant tasks can be performed using mobile devices. ERP system extended to have advanced reporting services, integrated with Marketing Automation and Customer Relationship Management (CRM).

The growth of investments in ERP solutions is an indication of how important this type of software for organizations, not only those working on production factories, but almost all industries. Any business consists of different functions; hence, the use of ERP solution and purchasing ERP modules – which we will come up to next – will depend on your organizational needs and what is meant to be achieved. The main business benefits of using an ERP system are:
The main goal of using ERP system is to centralize and share data between different departments and individuals in the organization to streamline business processes, while managers rely on ERP systems to analyze financial data, organizational performance and to improve decision-making processes.

As I mentioned earlier, ERP system consists of several modules, each to manage a specific function inside your organization. One of the main characteristics of an ERP system is its modularity, and the success of one depends on the ability and flexibility to fulfil organizations’ requirements with all their differences and customizations. A small business may just need an inventory and financial management systems, while a larger one may need in addition to that, a Human Resource, Payroll and Production management system.
Main ERP Modules can be summarized as follows:
We need to mention that sometimes CRM is not considered part of ERP system, but it can be easily integrated to ERP system to automate and streamline the business process.
Adopting an ERP solution itself does not guarantee its success in an organization. Purchasing an ERP solution must be consisted of and followed by well-formed implementation processes, which may involve some – if not all – of the following:
ERP implementation is a critical step toward the success of any ERP solution, no matter how good the solution is, or how many modules it consists.
ERP Implementation time varies, for small businesses it may take 6 months, and it may take a year for large businesses depending on business size, number of modules, customizations and how ready are the organization to take the wheel and go live.
Industries
What industries use ERP system? Simply we can say ERP system can cover any type of businesses as long as it has one of the functions mentioned in the ERP modules section. We may categorize these types of business in:
Trends

Every day’s inventions and new technologies have a great impact in the development of ERP systems. The most important trends we may heard about and is continuing to expand are:
Adopting an ERP solution may cost you money, but when implemented in the right way you’ll find a great potentiality to success. A great ERP system is the one fits you the most tied to the flexibility to changes and customizations.